Design Principles of Vue 3.0 by Evan You
VueJS optimizes for approachability and scalability
Folks from all different backgrounds decide to learn Vue.
- Beginners just progressing from HTML & CSS
- Professionals moving on from jQuery
- Veterans migrating from another framework
- Backend engineers looking for a lightweight frontend solution
- Architects choosing the foundation for an entire organization
Vue is scalable and supports a variety of use cases.
- Sprinkling interactivity onto legacy applications
- One-off projects which demand fast turn-around but no long-term maintenance concerns
- Medium scale apps where complexity cap is predictable
- Large scale projects expected to last for years with team churn
Library (e.g. React) vs Framework (e.g. Angular)
Small library pros:
- Fewer concepts to get started with
- More flexibility and more active ecosystem
- Smaller maintenance surface so the team can focus on exploring new ideas
Small library cons:
- More plumbing work needed by the developer
- Patterns emerge over time and become semi-required knowledge without really being documented
- Fast moving ecosystem can lead to fragmentation
Large framework pros:
- Most of the common problems can be solved with a built-in abstractions
- Centralized design process ensures consistent and coherent ecosystem
Large framework cons:
- Higher barrier to entry
- Inflexible if built-in solution doesn’t fit use case
- Larger maintenance surface makes introducing new ideas more costly
Vue tries to strike a balance between library and framework. Vue has a layered design that allows for features to be opted into in a progressive manner.
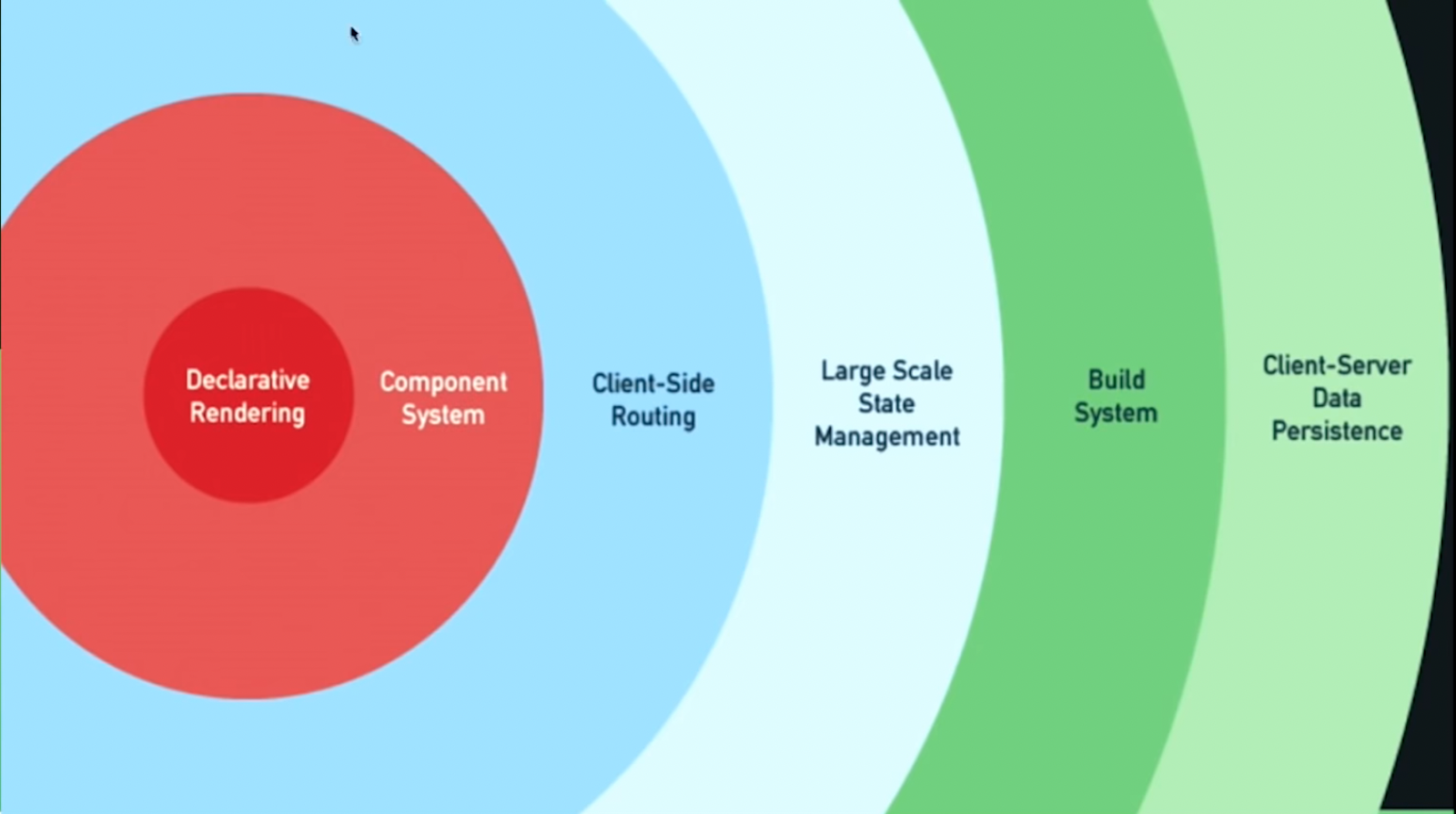
This gives the developer a low barrier to entry along with documented solutions for common problems.
Vue 3 features
The composition API is a purely additive feature of Vue 3 that provides a facility for us to better organize our code, reuse our code and leverage types in our code.
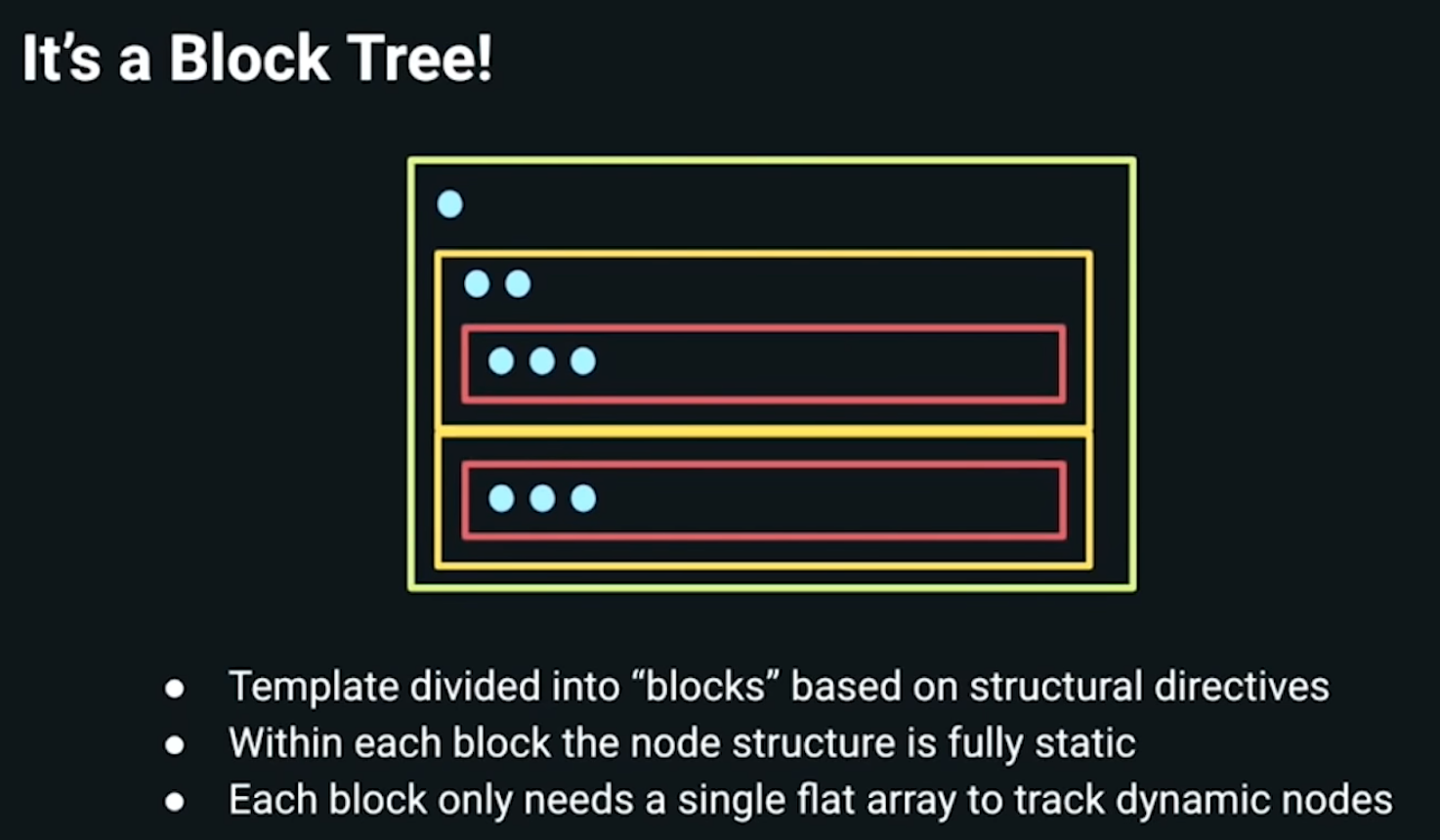
Vue 3 is more performant than Vue 2 and many other JS frameworks. Virtual DOM processing is efficiently accomplished via the “block tree” algorithm.
Vue 3 is much smaller in size than Vue 2. Most global APIs and internal helpers are tree-shakable ES module exports. Also, the compiler generates tree-shake-friendly code.
Vue 3 also comes with first-class custom renderer APIs as well as first-class custom compiler APIs to allow for even more low-level flexibility. Custom renderer APIs will make things like targeting different rendered outputs (mobile, terminal, etc.) much easier. Custom compiler APIs will make things like custom compile-time transformations (compile-time internationalization, compile-time accessibility, etc.) much easier.